Non-Metals On The Periodic Table
CONTENT INDEX
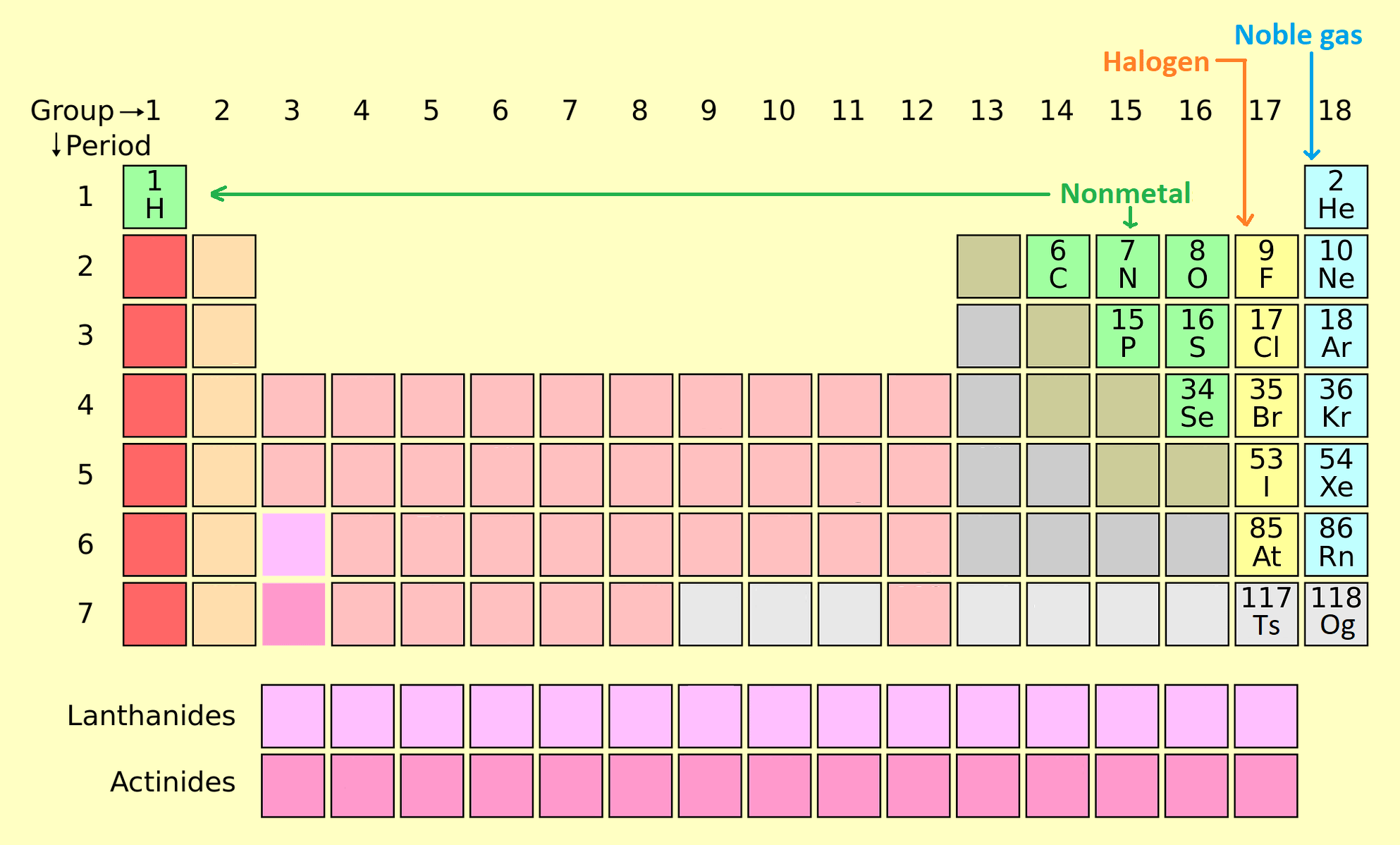
About Nonmetals
Total 20 nonmetals found in earth, They are normally existing as in solid or liquid or gaseous state at room temperature depend upon the element. These are usually brittle and non-lustrous in solid state. Here, we will discuss about chemical and physical properties of nonmetals, and about their uses in our daily life. We have also tell you about some interesting facts and many more thing of non-metals. So, let’s start with their occurrence and general properties.
Occurrence – Nonmetals are a group of elements located on the right side of the periodic table (other than hydrogen in the top of left).
General properties of Non-metals
- These elements are characterized by the fact that they usually have low melting and boiling points, do not conduct heat and electricity, and often have ionization energy and high electronegativity.
- It also doesn’t have the shiny “metallic” character associated with metals. Nonmetals tend to form brittle solids. Nonmetals tend to easily accept electrons to fill their electron shells, so their atoms often form negatively charged ions.
- There are 20 non-metals. At room temperature, the nonmetals are either solid or gases except bromine which is a liquid. In all nonmetals, 1 is in liquid state (bromine), 11 are in gaseous state (Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Fluorine, Helium, Neon, Chlorine, Argon, Krypton, Xenon, Radon), and others are in solid states (Iodine, Carbon, Sulfur, Phosphorus, Astatine etc..).
- First non-metal is hydrogen (H).
- There are 7 elements (Hydrogen (sometimes called alkali metal), Carbon, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulphur, Selenium) belongs to the non-metal group. There are two other groups of elements are Halogens and Noble gas, that can be referred to as non-metals.
These 20 Non-metals are following
These non-metals are the group of Polyatomic Nonmetals, halogens, and noble gases:
Polyatomic Nonmetals: Hydrogen (H), Carbon (C), Nitrogen (N), Oxygen (O), Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), Selenium (Se).
Halogens (Diatomic Nonmetals) are Fluorine (F), Chlorine (Cl), Bromine (Br), Iodine (I), Astatine (At), Tennessine (Ts),
Gaseous Nonmetals are Helium (He), Neon (Ne), Argon (Ar), Krypton (kr), Xenon (Xe), Radon (Rn), Oganesson (Og) (can act as a noble gas except that it would not be a gas under normal conditions).
**Include Silicon (Si) and Arsenic (As), they becomes 22 Nonmetals. But we have considered both in Metalloids.
Abundance of Non-Metals
Hydrogen is the most abundant element, with oxygen, carbon, and nitrogen, being the third, fourth and seventh elements respectively. Nitrogen and oxygen make up most of the earth’s atmosphere, with nitrogen making up 78% and oxygen about 21%. The four mass elements in the human body are other non-metals, such as oxygen (65%), carbon (18%), hydrogen (10%), and nitrogen (3%). Oxygen is the most abundant non-metallic element in the earth’s crust.
Physical Properties of Non-Metals
- Non-metals are gases at room temperature like helium, hydrogen and oxygen. Few nonmetals are solid like Sulphur, phosphorous and carbon.
- Carbon is non-metal that can exist in different allotropy. Diamond is the allotrope of carbon, it is the hardest natural substance and has a very high melting and boiling points. Graphite is another allotrope of carbon, it is a good conductor of electricity.
- Bromine is an only non-metal which is liquid at room temperature.
- Gallium (Ga) and Cesium (Cs) has very low melting points, but both are metals. They will melt if you keep them on your palm.
- Non-Metals are not very good at reflecting light. They are very dull except iodine.
- Iodine is a non-metal but it is lustrous.
- NonMetals produce acidic oxides when dissolve in water and metals gives rise to basic oxides.
- NonMetals are generally float in the water, This is because most nonmetals are lighter than water. That’s why we fill the balloons with nonmetals rather than metals.
- We mostly use helium to fill the balloons, this is because it is safer and less reactive than hydrogen.
- Non-metals are not good conductors of heat and electricity, while Graphite can conduct electricity, even though it is a non-metal.
- Nonmetals are brittle meaning they break easily. This also means that, they are not malleable.
- Nonmetals have low melting points, that’s why most of them are gases at room temperature.
- Non-metals show high ionization enthalpies and electronegativities.
Chemical Properties of Non-Metals
- Reaction of non-metals with oxygen: when they react with oxygen, they form non-metallic oxide. C + O2 → CO2
- Reaction with dilute acids: Nonmetals do not reacts with acids.
- They show electronegative character (tendency to gain electrons).
- Nonmetals have tendency to gain electrons and get reduced. Thus, they are strong oxidizing agents, Example: Fluorine.
- Formation of covalent compounds: They do share of electrons and form covalent compounds.
- Nonmetals do not react with water and hence do not displace hydrogen from water.
- Nonmetals react with hydrogen to form stable, covalent hydrides.
- Non-metals form covalent chlorides with chlorine.
Uses of Non-metals
Uses of Carbon
- Graphite is used to make pencil led. It has the perfect blend of hardness and blackness.
- Graphite is also used as waxing coating over surfaces. It can be used to provide protection against rust.
- Not only the graphite, diamond is also another allotrope of carbon. So, diamond is used as tool in grinding, drilling, cutting and polishing.
Uses of Nitrogen and Phosphorous
- It is used in fertilizers for better crop growth.
Uses of Oxygen
- This nonmetal plays a major role in a lifecycle.
- Life support for plants and animals.
Uses of phosphorous and Sulphur
- Phosphorous and sulfur are used in crackers and fireworks.
Nonmetals Facts
- Water molecule is made up of two non-metals, oxygen and hydrogen.
- Even counting halogens and noble gases, there are only 18 elements in the periodic table that are considered non-metallic.
- Many nonmetals can take on metallic properties under very high pressure.
- Selenium takes its name from the Greek word “Selene”, which means “moon”.
- Carbon is the only important element for life on earth.
- Fluorine does not have an Oxide.
- Lightning is responsible for 8% of nitrogen fixation on earth.
So, this was all about the non-metals. We have discussed above all the important information about the NonMetals like their abundance, physical and chemical properties. We have also discussed about the uses of NonMetals and some interesting facts which is related to non-metals. Thus, now I hope you get all the information properly about this topic.