23 V (Vanadium Element)

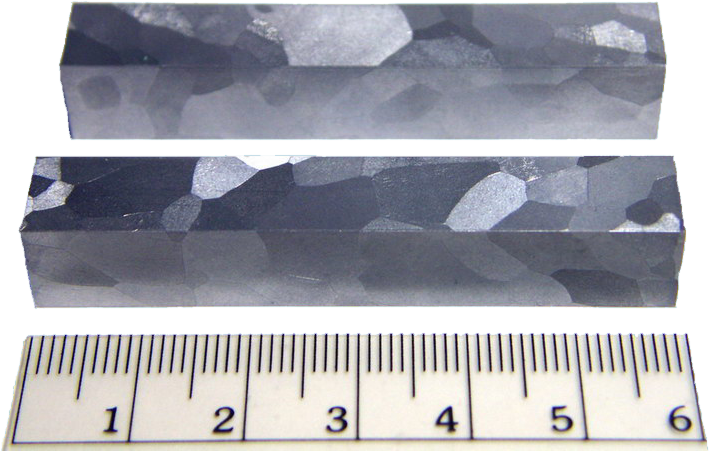
Pure vanadium is a rare, soft, ductile gray-white metal.
It has good corrosion resistance (due to a protective film of oxide on the surface) to alkalis, hydrochloric and sulfuric acid, and salt water, but the metal oxidizes readily above 660°C.

Identity
CAS Number: CAS7440-62-2
CID Number: CID23990
DOT Hazard Class: 4.1
DOT Number: 3089
CONTENT INDEX
Basic Properties of Vanadium
Pronunciation: Va-nay-dee-am
Appearance: Blue silver grey Metal
Mass Number: 51
Standard Atomic weight: 50.9415 g/mol
Atomic number (Z): 23
Electrons: 23
Protons: 23
Neutrons: 28
Period: 4
Group: 5
Block: d
Element category: Trasition metal
Electrons per shell: K2, L8, M11, N2
Electron configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p63d34s2

Thermal Properties of Vanadium
Phase: Solid
Melting point: 2183 K (1910 oC, 3470 oF)
Boiling point: 3680 K (3407 oC, 6165 oF)
Debye temperature: 390 K (116.85 oC, 242.33 oF)
Fusion heat: 21.5 kJ/mol
Vaporization heat: 444 kJ/mol
Specific heat: 489 J/(kg K)
Molar heat capacity: 24.88 J/(mol.K)
Thermal expansion: 8.4 μm/(m∙K)
Thermal conductivity: 30.6 W/(m∙K)
Electrical properties of Vanadium
Electrical conductivity: 5×106 S/m
A Electrical resistivity: 197 nΩ∙m
A Electrical type: Conductor
Critical point (Superconducting point): 5.4 K (-267.75 oC, -449.95 oF)
Magnetic Properties of Vanadium
A Magnetic type: Paramagnetic
Magnetic susceptibility (xmol): +255×10-6 cm3/mol
Volume magnetic susceptibility: 0.0003837
Mass magnetic susceptibility: 62.8×10-9 m3/kg
Molar magnetic susceptibility: 3.199×10-9 m3/mol
Physical Properties of Vanadium
Density: 6.0 g/cm3 (In solid) 5.5 g/cm3 (In Liquid at M.P)
Molar volume: 0.0000083374 m3/mol
Young’s modulus: 128 GPa
Shear modulus: 47 GPa
Mohs Hardness: 6.7
Bulk modulus: 160 GPa
Poisson ratio: 0.37
Vicker hardness: 628-640 MPa
Brinell hardness: 600-742 MPa
Sound Speed: 4560 m/s
Atomic Properties of Vanadium
Oxidation states: -3,-1, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Valence Electrons: 3d3 4s2
Ion charge: V3+ V5+
Ionization potential of an atom: 6.76
Ionization energies: 1st: 651 kJ.mol 2nd: 1414 kJ/mol 3rd: 2830 kJ/mol
Ionic radius: 59 pm
Atomic radius: 134 pm (empirical)
Van der Waals: 179 Pm
Covalent radius: 153±8 pm
Filling Orbital: 3d3
Crystal structure: Body centered cubic
Lattice angles: π/2, π/2, π/2
Lattice constant: 302.4, 302.4, 302.4 pm
Grid parameters: a=3.024 Å
Space Group Name: Im_3m
Space Group Number: 229
Reactivity of Vanadium
Electronegativity: 1.63 (pauling scale)
Valence: +5
Electron affinity: 50.6 kJ/mol
Nuclear Properties of Vanadium
Half Life: Stable (Infinity)
Lifetime: Stable (Infinity)
Quantum Number: 4F3/2
Neutron cross section (Brans): 5.06
Neutron Mass Absorption: 0.0033
Isotopes: 48V 49V 50V 51V
| Isotope | Abundance (%) | Atomic Mass g/mol | Half Life (t1/2) |
| 48V | Syn | – | 16 d |
| 49V | Syn | – | 330 d |
| 50V | 0.25 | 49.946 | 1.5×1017 y |
| 51V | 99.75 | 50.944 | Stable |
Chemical Reactions of Vanadium
Vanadium metal reacts with excess oxygen (O2), and upon heating It form vanadium(V) oxide (V2O5). In this way (V2O5) is sometimes contamined by other vanadium oxides.
4 V (s) + 5 O2 (g) → 2 V2O5 (s) [yellow-orange]
It does not react with water
Reacts with fluorine (F2) when heated, It forms:
2 V (s) + 5 F2 (g) → 2 VF5 (I) [colourless]
Vanadium History
Naming: Nils Gabriel Sefstrom (1830)
Discovery: Andres Manuel del Rio (1801)
First isolation: Nils Gabriel Sefstrom (1830)
Vanadium Uses
It is used in producing high speed steel tools (rust resistant), and It is an important carbide stabilizer in making steels.
About 80% of the vanadium is used as a steel alloy called ferrovanadium.
Vanadium-steel alloys are very tough and are used for tools, axles, armour plate, piston rods, gears, crankshafts, and other critical components.
Steel alloys with little chromium and less than 1% of vanadium makes steel shock resistant and vibration resistant.
Titanium alloys mixed with aluminum & vanadium is used in jet engines and high speed air-frames.
AVanadium has low neutron-absorbing properties, even it doesn’t deform in creeping under high temperatures, so Vanadium alloys are used in nuclear reactors.
Vanadium (V) oxide (V2O5) is used as a catalyst in manufacturing sulfuric acid (H2SO4) and maleic anhydride (C4H2O3), as a pigment for ceramics and glass (green or blue tint), and in producing superconducting magnets with a field of 175,000 gauss.
Vanadium di-oxide (VO2) with Glass coated, can block infrared radiation at some specific temperature.
Biological role of Vanadium
AVanadium is essential for some species (including humans), although we need very little (around we daily intake only just 0.01 mg (milligrams)), which is more sufficient for our needs.
Vanadium and its compounds are Toxic and it should be handled with care.
Abundance of Vanadium
AVanadium is found in about 65 different minerals including Vanadinite (Pb5(VO4)3Cl), Roscoelite (K(V3+,Al,Mg)2AlSi3O10(OH)2), Carnotite (K2(UO2)2; (VO4)2·3H2O) and Patronite (Vanadium sulfide, VS4)
It is also found in phosphate rock (phosphorite) and certain iron ores, and is present in some crude oils in the form of organic complexes (any molecules that are composed of the element carbon).
Commercialy, The metal is obtained by reducing vanadium (V) oxide (V2O2) with calcium in a pressure vessel (a container designed to hold material at high pressures).
High-purity ductile vanadium can be obtained by reduction of vanadium (III) chloride (VCl₃) with magnesium (Mg) or with magnesium-sodium (Mg-Na) mixtures.
Annual world wide production is around 90,000 tons.
0.0001% (In Universe)
0.0061% (In Meteorites)
0.00004% (In Sun)
0.019% (In Earth’s Crust)
1.5×10-7% (In Oceans)
3×10-6% (In Humans)




World’s Top 3 producers of Vanadium
1) South Africa
2) China
3) Russia
World’s Top 3 Reserve holders of Vanadium
1) China
2) Russia
3) South Africa
#Vanadium



Greetings.
Thank you so much for this elements shortcards.
I came here accidently for information about ELEMENT 115 which is
linked to ET ship reactors / Bob Lazar…
Have a nice day
I know alien technology very well. Machines which are alive not just chemistry , electronics and mechanics.
It’s not friendly at all to display that on movies or pictures. it would rip millions of human minds apart and put them in a coma they will never wake up from.
Still the question about element 115 is not clear.
Do you ever heard the words black goo; replicators e.t.c?
https://spectrum.ieee.org/tech-talk/energy/nuclear/boeing-patents-laser-nuclear-fusion-jet-engine
Still nowhere enough to travel outside of the earth’s magnetic field.they call it space station which is fake. It’s technically a orbit spation. A legitimately word for a space station is if is outside of the earth magnetic field.the radiation from the sun is deadly.there has not been found out a ligth material to shield space travellers from the sun’s and the cosmic background radiation yet.and spaceships can not have a 2 meters thick LEAD layer….
A new material very ligth needs to be found.
And there are a few other NECESSITIES for space travel.