SSC Junior Engineer (JE) Exam Paper – 2018 “held on 22 January 2018” Morning Shift (Civil Engineering)
Q1: Which of the following represent the crushing strength (MPa) for the good quality stone that are used in the construction of buildings?
Options:
1) Less than 20
2) 20 to 60
3) 60 to 80
4) Greater than 100
Answer: Greater than 100
Q2: Which of the following is examined to determine the age of timber?
Options:
1) Annular ring
2) Sapwood
3) Pith
4) Timber defects
Answer: Annular ring
Q3: Which of the following is determined with the help of Le Chatelier’s device?
Options:
1) Abrasion resistance
2) Chemical resistance
3) Soundness
4) Strength
Answer: Soundness
Q4: The type of mortar which is used for the construction works carried out in water-logged area is _____.
Options:
1) cement mortar
2) loose mortar
3) mortar of very low consistency
4) mortar having high w/c ratio
Answer: cement mortar
Q5: For M 25 grade concrete, the split tensile strength in terms of percentage of its compressive strength is _____.
Options:
1) 7 to 11%
2) 18 to 28%
3) 28 to 38%
4) 38 to 48%
Answer: 7 to 11%
Q6: Distempers are generally used to coat _____.
Options:
1) compound wall
2) external concrete surfaces
3) interior surface which are not exposed to environment
4) wood works
Answer: interior surface which are not exposed to environment
Q7: Which of the following is commonly used as retarder in cement?
Options:
1) Calcium sulphate
2) Gypsum
3) Potassium carbide
4) Sodium chloride
Answer: Gypsum
Q8: In the process of hydration of OPC, to complete all chemical reaction, the water requirement (expressed as the percentage of cement) is _____.
Options:
1) 5 to 8%
2) 8 to 16%
3) 20 to 25%
4) 35 to 45%
Answer: 20 to 25%
Q9: The slump test is performed to check the _____.
Options:
1) presence of water in cement
2) ratio of concrete ingredients
3) temperature resistance
4) workability of concrete
Answer: workability of concrete
Q10: The reason behind the low expansion and shrinkage of the plywood is _____.
Options:
1) plies are placed at the right angles with each other
2) they are glued under the high pressure
3) they are held in the position with the help of adhesives
4) they are prepared with the help of veneers
Answer: plies are placed at the right angles with each other
Q11: Which one of the following method is used for the approximate estimation?
Options:
1) Both central line and short wall and long wall method
2) Central line method
3) Plinth area method
4) Short wall and long wall method
Answer: Plinth area method
Q12: Accuracy in the measurement of the thickness of the slab or sectional dimension of column and beam (in centimetre) should be _____.
Options:
1) 0.5
2) 1
3) 5
4) 10
Answer: 0.5
Q13: Deduction at T-junction of the wall for total length of the central line is _____.
Options:
1) half of thickness of wall
2) no deduction
3) thickness of wall
4) twice of the thickness of wall
Answer: half of thickness of wall
Q14: For estimation of painted area of semi corrugated asbestos cement sheets, percentage increase in area above plain area is _____.
Options:
1) 0.1
2) 0.14
3) 0.2
4) 0.25
Answer: 0.1
Q15: Scrap value of a property may be _____.
Options:
1) both negative or positive
2) constant
3) negative
4) positive
Answer: both negative or positive
Q16: What is the unit of measuring cornice?
Options:
1) Cubic metre
2) Number
3) Running metre
4) Square metre
Answer: Running metre
Q17: Calculate the number of bricks in 20 cubic metres brick works.
Options:
1) 500
2) 1000
3) 10000
4) 100000
Answer: 10000
Q18: Calculate the area (square metre) of the formwork required for a beam of 2 m span and cross section dimension of 400 mm x 200 mm.
Options:
1) 0.8
2) 0.16
3) 1.2
4) 2
Answer: 2
Q19: The cross section areas of three sections of an embankment at an interval of 40 m are 10 square metres, 15 square metres and 35 square metres. Calculate the quantity of earthwork for the embankment. Use prismoidal method.
Options:
1) 1200
2) 1400
3) 1500
4) 2400
Answer: 1400
Q20: Calculate the annual depreciation (Rs.) of a machine having initial cost of Rs. 10,000. The scrap value is Rs. 1,000 and useful life of 30 years.
Options:
1) 300
2) 367
3) 1333
4) 333333
Answer: 300
Q21: What is the difference between the sum of interior angles of plane triangle and spherical triangle for area of triangle 195 square kilometre on the Earth’s surface?
Options:
1) one degree
2) one minute
3) one second
4) one radian
Answer: one second
Q22: Which one of the following is the largest scale?
Options:
1) 1 :500
2) 1 :1000
3) 1 :2500
4) 1 :50000
Answer: 1 :500
Q23: The quadrantal bearing of the line lies in the third quadrant making angle in clockwise with the north is ______.
Options:
1) N(θ – 180)oE
2) N(θ – 180)oW
3) S(θ – 180)oE
4) S(θ – 180)oW
Answer: S(θ – 180)oW
Q24: Calculate the volume of the embankment (in cubic metre) using trapezoidal method, if the cross section areas of the three sections of an embankment at an interval of 30 m are 20 square metres, 40 square metres and 50 square metres.
Options:
1) 1100
2) 1150
3) 2250
4) 2350
Answer: 2250
Q25: Which one is the CORRECT order of the tapes based on their accuracy?
Options:
1) Linen tape > invar tape > metallic tape > steel tape
2) Invar tape > steel tape > metallic tape > linen tape
3) Metallic tape > steel tape > linen tape > invar tape
4) Metallic tape > steel tape > Invar tape > linen tape
Answer: Invar tape > steel tape > metallic tape > linen tape
SSC Junior Engineer All Previous Papers
Q26: In the leveling between two points A and B on the opposite sides of a pond, the level is first set up near the point A and staff reading on A and B are 2.5 m and 2.0 m respectively. Then the level is moved and set near the point B, staff reading on points A and B are 1.2 m and 1.7 m respectively. Calculate the difference of heights between the two points A and B (in metre).
Options:
1) 0
2) 0.5
3) 1
4) 1.85
Answer: 0
Q27: Calculate the combined correction for curvature and refraction (in m) for a distance of 2 km.
Options:
1) 0.045
2) 0.135
3) 0.269
4) 3.14
Answer: 0.269
Q28: In transit theodolite, the line of the sight can be reversed by revolving the telescope through _____.
Options:
1) 90° in horizontal plane
2) 90° in vertical plane
3) 180° in horizontal plane
4) 180° in vertical plane
Answer: 180° in vertical plane
Q29: Which one is the CORRECT sequence for the temporary adjustment of the theodolite?
Options:
1) Centering, elimination of parallax, leveling, and setting
2) Centering, setting, elimination of parallax and leveling
3) Setting, centering, leveling and elimination of parallax
4) Setting, leveling, elimination of parallax and centering
Answer: Setting, centering, leveling and elimination of parallax
Q30: Which of the following is used for determining the location of station occupied by the plane table?
Options:
1) Both intersection and radiation
2) Intersection method
3) Radiation method
4) Two point problem
Answer: Two point problem
Q31:– Which of the following is responsible for the formation of residual soil?
Options:
1) Glaciers
2) Water
3) Wind
4) None of these
Answer: None of these
Q32: The coefficient of gradation and the coefficient of uniformity of a given soil sample is 1.0 and 4.0 respectively. The ratio of effective size to the diameter through which 30% of the total mass is passed is ______.
Options:
1) 1.25
2) 1.5
3) 1.75
4) 2
Answer: 2
Q33: Which of the following shows the CORRECT order of increasing surface areas of the given soil?
Options:
1) Clay < silt < sand < colloids
2) Gravel < silt < colloids < clay
3) Sand < silt < clay < colloids
4) Silt < gravel < colloids < clay
Answer: Sand < silt < clay < colloids
Q34: What is the assumption made about back of wall, in the Rankine’s theory of earth pressure?
Options:
1) Plane and rough
2) Plane and smooth
3) Vertical and rough
4) Vertical and smooth
Answer: Vertical and smooth
Q35: Which of the following is CORRECT about the viscosity of gas?
Options:
1) Inversely proportional to the temperature
2) Increases with an increase in the temperature
3) Independent of pressure
4) Independent of temperature
Answer: Increases with an increase in the temperature
Q36: Pressure of 200 kPa is equivalent to the head of z metre of liquid having relative density 1.59. The value of z (m) is _____.
Options:
1) 11.6
2) 11.82
3) 12.82
4) 13.14
Answer: 12.82
Q37: Which one of the following statement is CORRECT about the center of buoyancy?
Options:
1) It is the point where buoyant force act.
2) It coincides with the centroid of volume of water displaced
3) It is the point where buoyant force act. and It coincides with the centroid of volume of water displaced
4) It acts outside the body.
Answer: It is the point where buoyant force act. and It coincides with the centroid of volume of water displaced
Q38: A longitudinal rectangular surface is hanged into the water such that its top and bottom points are at depth of 1.5 m and 6.0 m respectively. The depth of center of pressure (m) from the top surface is _____.
Options:
1) 3.8
2) 4.2
3) 4.6
4) 4.8
Answer: 4.2
Q39: The velocity potential which follow the equation of continuity is _____.
Options:
1) x2y
2) x2 – y2
3) cos x
4) x2 + y2
Answer: x2 – y2
Q40: At what distance from the boundary layer, the value of the wall shear is three times of the turbulent shear?
Options:
1) 1/3 R
2) 1/2 R
3) 2/3 R
4) 3/4 R
Answer: 2/3 R
Q41: Which of the following statement is CORRECT about the stream lines and equipotential lines?
Options:
1) Both can be drawn graphically for viscous flow around any boundary.
2) Meshes formed by them are always squares.
3) They always meet orthogonally.
4) They can be calculated for all boundary conditions.
Answer: They always meet orthogonally.
Q42: The Rankine half oval body MM is subjected to the two-dimensional flow having velocity V. The typical stream line is shown in the following diagram. The point A in diagram shows________.
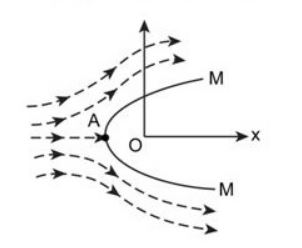
Options:
1) point at which velocity is maximum
2) separation point
3) stagnation point
4) stall point
Answer: stagnation point
Q43:Which of the following is CORRECT ratio for Froude number?
Options:
1) Compressive force to inertia force.
2) Inertia force to gravity force.
3) Inertia force to tension force.
4) Viscous force to inertia force.
Answer: Inertia force to gravity force.
Q44: For the most economical triangular channel section, the angle of sloping sides from the vertical is _____.
Options:
1) 30o
2) 45o
3) 60o
4) 75o
Answer: 45o
Q45: Method of applying water directly to the root zone of the plant is called _____.
Options:
1) check flooding
2) drip method
3) furrow method
4) sprinkler irrigation
Answer: drip method
Q46: A field of 500 hectares is to be irrigated for a particular crop having 100 days base period. The total depth of water required by the crop is 100 cm. Calculate the duty of the water (in hectares per cubic metre).
Options:
1) 8.64
2) 57.87
3) 86.4
4) 864
Answer: 864
Q47: The traffic volume of a roadway is defined as the multiplication of _____.
Options:
1) speed and time headway
2) speed and distance way
3) traffic density and speed
4) time head way and distance headway
Answer: traffic density and speed
Q48: Calculate the equivalent radius (cm) of the resisting section of 20 cm slab, if the ratio of radius of wheel load distribution to the thickness of the slab is 2.
Options:
1) 20
2) 35.6
3) 40
4) 40.9
Answer: 40
Q49: On peak hourly demand, what is the maximum daily consumption for the city which have average daily consumption of 100,000 m3 ?
Options:
1) 140000
2) 170000
3) 200000
4) 270000
Answer: 270000
Q50: For which of the following, distribution mains is designed?
Options:
1) Average daily demand
2) Annual peak demand
3) Monthly peak demand
4) Maximum hourly demand on maximum day
Answer: Maximum hourly demand on maximum day
SSC Junior Engineer All Previous Papers
Q51: Which of the following statements is true?
A.Most of the loads applied to a building are environmental load.
B. Most of the loads are dead followed by live loads.
Options:
1) Only A
2) Only B
3) Both A and B
4) Neither A nor B
Answer: Only B
Q52: How does an increase in the pitch of the roof affects the amount of load that can be placed on it?
Options:
1) It increases
2) It decreases
3) Remains constant
4) Depends upon case
Answer: It decreases
Q53: What will be the rain load (in psf) if ds is 2 inches and dh is 1 inches?
Options:
1) 5.2
2) 10.4
3) 15.6
4) 20.8
Answer: 15.6
Q54: Concrete is:-
Options:
1) Good in compression, good in tension
2) Good in compression, weak in tension
3) Weak in compression, weak in tension
4) Weak in compression, good in tension
Answer: Good in compression, weak in tension
Q55: If in planar system, X parts/members are there with Y no. of forces, then condition for statically determinacy is:-
Options:
1) Y < 3X
Y < 3X
2) Y > 3X
Y > 3X
3) Y= 3X
Y= 3X
4) None of these
Answer: Y= 3X
Y=3X
Q56: If a system has more equations of equilibrium than no. of forces, then the system is:-
Options:
1) Improperly constrained
2) Partially constrained
3) Stable
4) None of these
Answer: Partially constrained
Q57: Which of the following material is not used in making trusses?
Options:
1) Wooden struts
2) Metal bars
3) Channel
4) Concrete
Answer: Concrete
Q58: In a truss it is assumed that the members are joined by____________.
Options:
1) Rough pins
2) Smooth pins
3) Either rough or smooth pins
4) None of these
Answer: Smooth pins
Q59: What is the major difference between truss and beam?
Options:
1) Beam can’t transmit load in vertical direction while truss can
2) Truss can’t transmit load in vertical direction while beam can
3) Beam can’t transmit load in axial direction while truss can
4) Truss can’t transmit load in axial direction while beam can
Answer: Truss can’t transmit load in vertical direction while beam can
Q60: Given that J is no. of joints. B and R are no. of members and no. of reactions.
If B = 4, R = 3 and J = 4, then the truss is:-
Options:
1) Statically determinate
2) Statically indeterminate and stable
3) Stable
4) Unstable
Answer: Unstable
Q61: Which IS code gives details regarding water to be used in concrete?
Options:
1) IS 456
2) IS 383
3) IS 565
4) IS 3012
Answer: IS 456
Q62: Which of the below is an example of plasticizer?
Options:
1) Hydroxylated carboxylic acid
2) Fluoro-silicate
3) Gypsum
4) Surkhi
Answer: Hydroxylated carboxylic acid
Q63: How many methods of batching of concrete are there?
Options:
1) 2
2) 3
3) 5
4) 6
Answer: 2
Q64: Concrete is generally placed on a:
Options:
1) Form work
2) Stand
3) Mould
4) Platform
Answer: Form work
Q65: The effective width of a column strip of a flat slab is taken as
Options:
1) one-fourth the width of the panel
2) half the width of the panel
3) half the diameter of the column
4) the diameter of the column
Answer: half the width of the panel
Q66: Permanent dimension changes due to loading of concrete is termed as:
Options:
1) Strain
2) Extent
3) Creep
4) Ambit
Answer: Creep
Q67: In design of R.C.C. structures, the tensile strength of concrete is taken as:
Options:
1) 5N/mm2
2) 2N/mm2
3) 0.3N/mm2
4) None of these
Answer: None of these
Q68: Flexure strength of concrete is determined as:
Options:
1) Modulus of rigidity
2) Modulus of rupture
3) Modulus of plasticity
4) Modulus of elasticity
Answer: Modulus of rupture
Q69: Properties of concrete can broadly be divided into:
Options:
1) 1
2) 4
3) 2
4) 3
Answer: 2
Q70: Which IS code gives specifications about cement plaster?
Options:
1) IS 1500
2) IS 1221
3) IS 1400
4) IS 1661
Answer: IS 1661
Q71: In a lime-cement plaster, ratio 1:1:6 corresponds to:
Options:
1) Lime:cement:sand
2) Cement:Lime:sand
3) Lime:sand:gravel
4) Cement:sand:gravel
Answer: Cement:Lime:sand
Q72: On which of the following does the correct proportion of ingredients of concrete depend upon?
Options:
1) bulking of sand
2) water content
3) absorption and workability
4) All option are correct
Answer: All option are correct
Q73: If X, Y and Z are fineness moduli of coarse fine and combined aggregates, the percentage (P) of fine aggregates to combined aggregates is
Options:
1) P = (z-x / z-y) x 100
2) P = (x-z / z-y) x 100
3) P = (x-z / z+y) x 100
4) P = (x+z / z-y) x 100
Answer: P = (x-z / z-y) x 100
Q74: Which of the following statements is false?
Options:
1) Workability of the concrete mix decreases with an increase in the moisture content
2) Concrete for which preliminary tests are conducted, is called controlled concrete
3) Bulking of sand depends upon the fineness of grains
4) All option are correct
Answer: All option are correct
Q75: Which of the following statements is false?
Options:
1) Space between the exterior walls of a warehouse and bag piles should be 30 cm
2) Cement bags should preferably be piled on wooden planks
3) Cement bags should be placed such that bags of one layer does not touch the bags of the adjacent layer
4) None of these
Answer: None of these
SSC Junior Engineer All Previous Papers
Q76: Which of the following statements is false?
Options:
1) With passage of time, the strength of cement increases
2) With passage of time, the strength of cement decreases
3) After a period of 24 months, the strength of cement reduces to 50%
4) The concrete made with storage deteriorated cement gains strength with time
Answer: With passage of time, the strength of cement increases
Q77: For a concrete mix 1:3:6 and water cement ratio 0.6 both by weight, what is the quantity of water required per bag?
Options:
1) 10 kg
2) 12 kg
3) 14 kg
4) None of these
Answer: 14 kg
Q78: Transport of concrete by pumps, is done for a distance of
Options:
1) 100 m
2) 200 m
3) 300 m
4) 400 m
Answer: 400 m
Q79: The compression in PSC is done by _________ of high-strength tendons.
Options:
1) Compression
2) Tensioning
3) Shearing
4) Bending
Answer: Tensioning
Q80: In which beam tension capacity of steel is greater than combined compression capacity of steel and concrete?
Options:
1) Over-reinforced
2) Under-reinforced
3) Singly reinforced
4) Doubly reinforced
Answer: Over-reinforced
Q81: A simply support beam carries a varying load from zero at one end and w at the other end. If the length of the beam is a, the maximum bending moment will be
Options:
1) wa / 27
2) wa2 / 27
3) w2a / √27
4) wa2 / 9√3
Answer: w2a / √27
Q82: For a circular slab carrying a uniformly distributed load, the ratio of the maximum negative to maximum positive radial moment is
Options:
1) 1
2) 2
3) 3
4) 4
Answer: 2
Q83: If W is total load per unit area on a panel, D is the diameter of the column head, L is the span in two directions, then the sum of the maximum positive bending moment and average of the negative bending moment for the design of the span of a square flat slab, should not be less than
Options:
1) (WL / 12) (L – 2D/3)2
2) (WL / 10) (L + 2D/3)2
3) (WL / 10) (L – 2D/3)2
4) (WL /12) (L – D/3)2
Answer: (WL / 10) (L – 2D/3)2
Q84: The breadth of a ribbed slab containing two bars must be between
Options:
1) 6 cm to 7.5 cm
2) 8 cm to 10 cm
3) 10 cm to 12 cm
4) None of these
Answer: 8 cm to 10 cm
Q85: A foundation rests on which of the following?
Options:
1) base of the foundation
2) sub grade
3) foundation soil
4) Both Sub grade and foundation soil
Answer: Both Sub grade and foundation soil
Q86: Which of the following statements is true?
Options:
1) To ensure uniform pressure distribution, the thickness of the foundation is kept uniform throughout
2) To ensure uniform pressure distribution, the thickness of the foundation is increased gradually towards the edge
3) To ensure uniform pressure distribution, the thickness of the foundation is decreased gradually towards the edge
4) To ensure uniform pressure distribution, the thickness of the foundation is kept zero at the edge
Answer: To ensure uniform pressure distribution, the thickness of the foundation is decreased gradually towards the edge
Q87: The weight of a foundation is assumed as which of the following?
Options:
1) 5% of wall weight
2) 7% of wall weight
3) 10% of wall weight
4) 12% of wall weight
Answer: 10% of wall weight
Q 88: If the width of the foundation for two equal columns is restricted, the shape of the footing generally adopted is
Options:
1) Square
2) rectangular
3) trapezoidal
4) triangular
Answer: rectangular
Q89: Maximum shear stress theory for the failure of a material at the elastic limit is known as
Options:
1) Guest’s or Trecas’ theory
2) St.Venant’s theory
3) Rankine’s theory
4) Haig’s theory
Answer: Guest’s or Trecas’ theory
Q90: If permissible compressive stress in concrete is 50 kg/cm2, tensile stress in steel is 1400 kg/cm2 and modular ratio is 18, the depth of the beam is
Q91: When not specified, the volume of steel in R.C.C. work is taken as:-
Options:
1) 1% to 1.6% of R.C.C. volume
2) 2% to 4% of R.C.C. volume
3) 4% to 6% of R.C.C. volume
4) 0.6% to 1% of R.C.C. volume
Answer: 0.6% to 1% of R.C.C. volume
Q92: The ratio of maximum shear stress to average shear stress of a circular beam is:
Options:
A. 2/3
B. 3/2
C. 3/4
D. 4/3
Answer: 4/3
Q93: The property of a material by which it can be beaten or rolled into plates, is called
Options:
1) ductility
2) plasticity
3) elasticity
4) None of these
Answer: None of these
Q94: What is the limit to Poisson’s ratio?
Options:
1) 0.1
2) 0.2
3) 0.3
4) None of these
Answer: None of these
Q95: Among the following, which is least elastic?
Options:
1) Iron
2) Copper
3) Both Copper and Silver
4) Rubber
Answer: Rubber
Q96: Two bars of different materials are of the same size and are subjected to same tensile forces. If the bars have unit elongations in the ratio of 4 : 7, then the ratio of modulius of elasticity of the two materials is
A. 4:7
B. 4:10
C. 16:49
Options:
1) A Only
2) B Only
3) C Only
4) None of these
Answer: None of these
Q97: If a composite bar of steel and copper is heated, then the copper bar will be under:
Options:
1) tension
2) shear
3) torsion
4) None of these
Answer: None of these
Q98: Pick up the incorrect statement from the following : The torsional resistance of a shaft is directly proportional to
Options:
1) modulus of rigidity
2) angle of twist
3) reciprocal of the length of the shaft
4) moment of inertia of the shaft section.
Answer: moment of inertia of the shaft section.
Q99: Net sectional area of a tension member, is equal to its cross section area_______.
Options:
1) plus the area of the rivet holes
2) divided by the area of rivet holes
3) multiplied by the area of the rivet holes
4) minus the area of the rivet holes
Answer: minus the area of the rivet holes
Q100: When a tension member consists of two channel sections, the allowance for rivet hole is made for two holes from
Options:
1) each web
2) each flange
3) each web or one hole from each flange whichever is more
4) each web or one hole from each flange whichever is less
Answer: each web or one hole from each flange whichever is less




